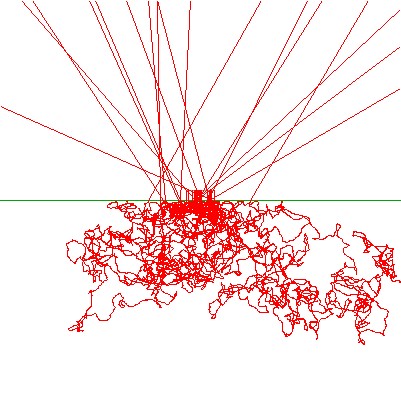
The following simple SPRAY model is used to simulate a diffuse reflectance experiment: A circular (transparent) light source illuminates an interface from air to a solid material (binder). The binder contains spherical pigments with an absorption band in the visible spectral range. The binder itself absorbs in the UV. On top is a huge rectangular detector collecting all rays that esape into the upper halfspace.
Here is a side view of the system not showing the detector:
The optical constants of the pigments are the following:
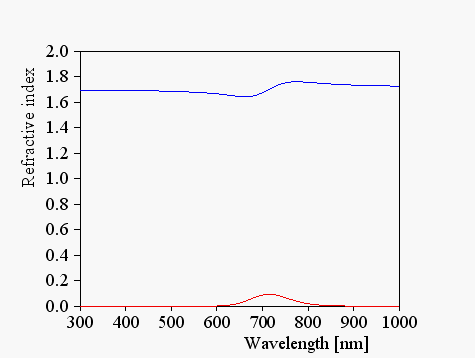
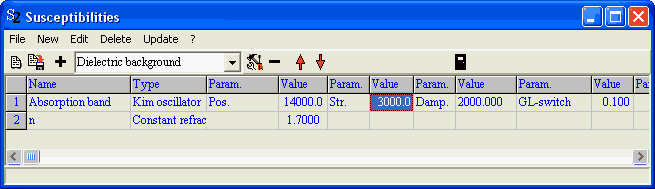
They are computed based on a constant and a Kim oscillator:
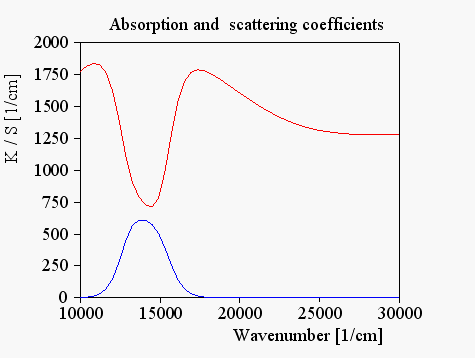
The scattering and absorption coefficients are computed using an extended Mie scatterer object with the following result:
The corresponding diffuse reflectance spectrum has been computed with 30 spectral points in the range 300 ... 1000 nm sending 1000 rays at each spectral points:
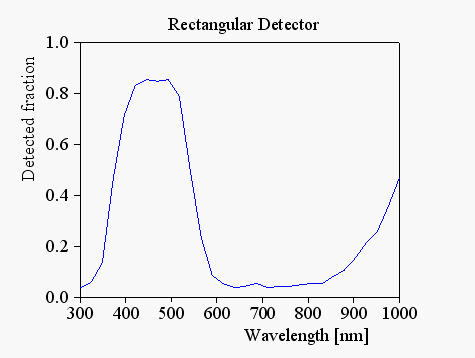
This spectrum is saved in the file measured_spectrum.std using the standard data format. It will serve as the 'measurement' in the following fit procedure.