Open the list of materials and generate a new object of type 'Interpolate n and k tables'. Open this object and
•execute the menu command 'Master parameter / change name' and set the name of the parameter to 'q' (for charge).
•execute the 'Range' command and set 200 points, covering the wavelength range 300 ... 2500 nm.
•Click on 'Tables / n' to open the following subwindow:
In this window we are going to collect the n data.
Importing data from single files
Use the command 'New and import' to read data from a file that has been generated as explained in the last section. For text files with 2 columns (wavelength, n) use the import filter 'xy-format (spreadsheet)'. After the file has been selected press 'a' on your keyboard for automatic scaling of the graph:
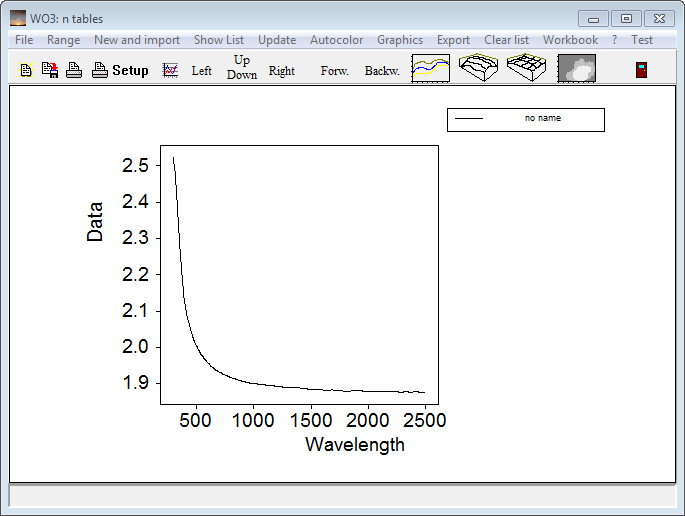
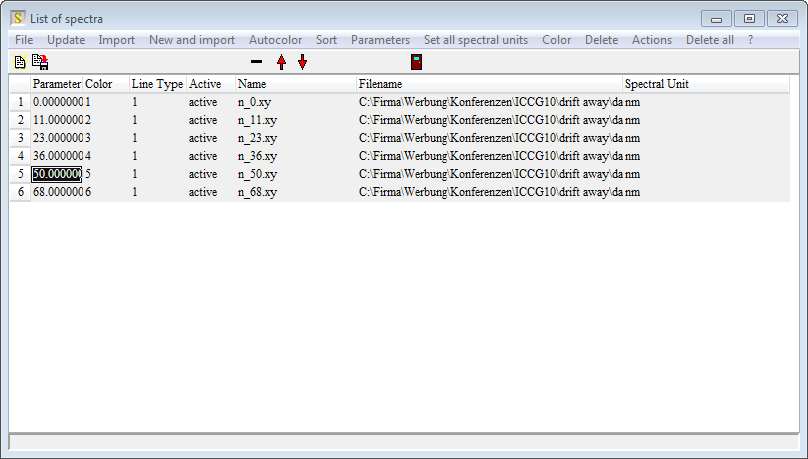
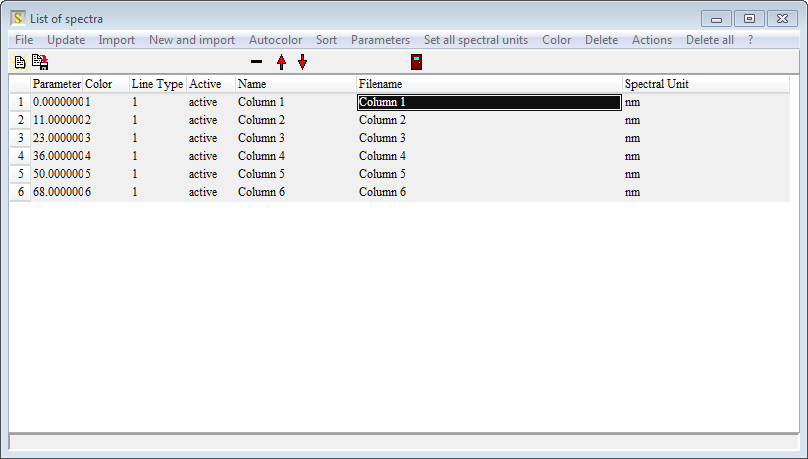
A click on 'Show list' opens the list of spectra:
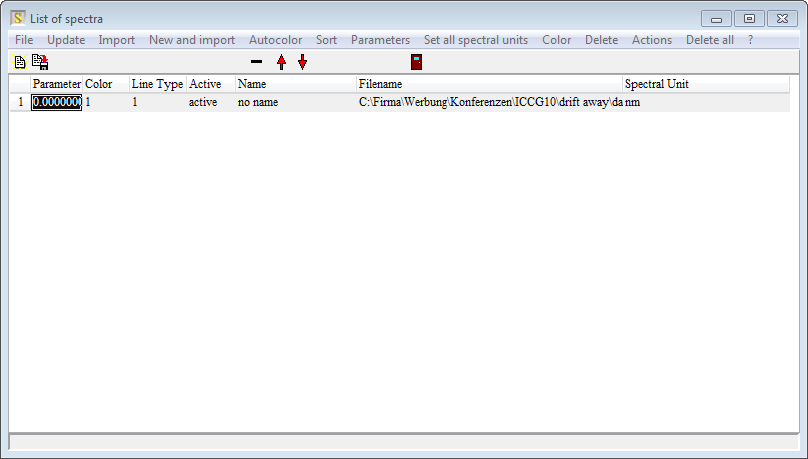
Click on 'Actions/ Set filenames as spectrum names' - this replaces the noname name by the filename without path. Repeat the data import for all files that you have:
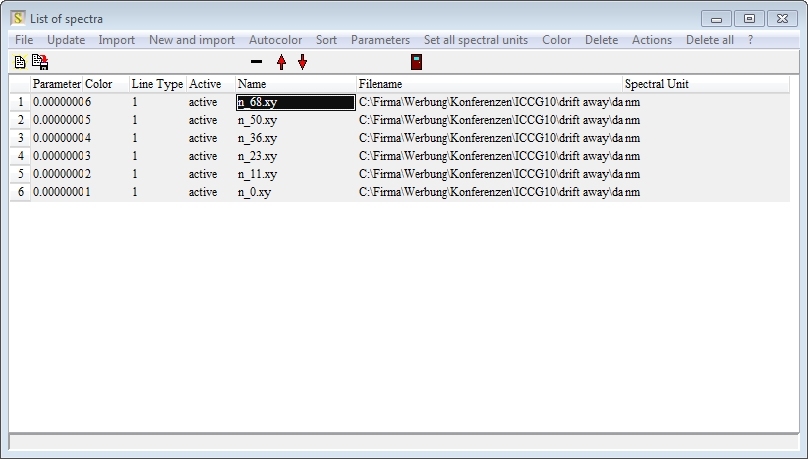
Now, finally, type in the parameter values that belong to the files into the first column (Parameter). Click on Sort and verify that your table looks like this:
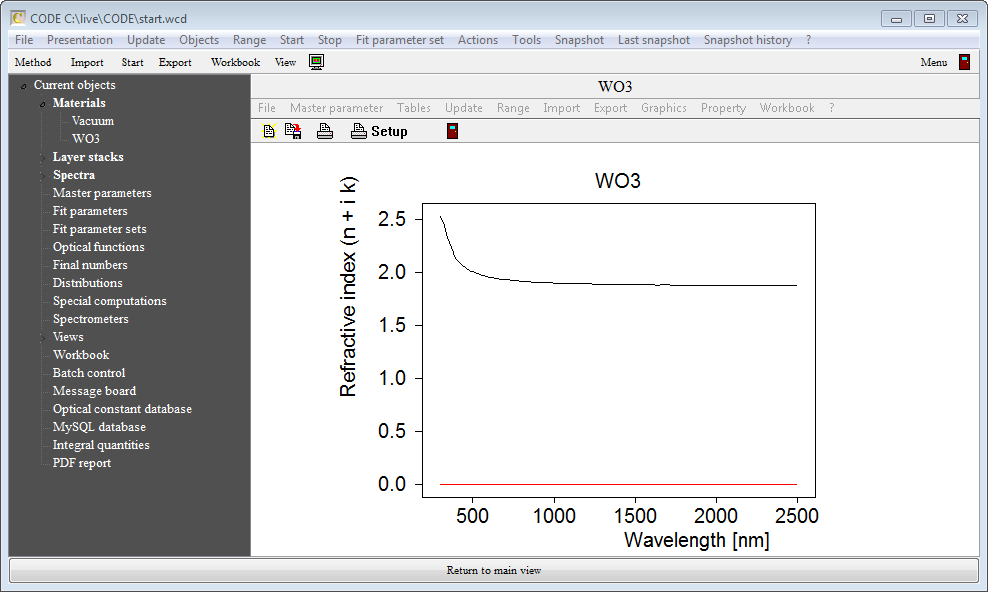
Close the n table and return to the new material object. Pressing 'a' for automatic scaling should lead to a graph like this:
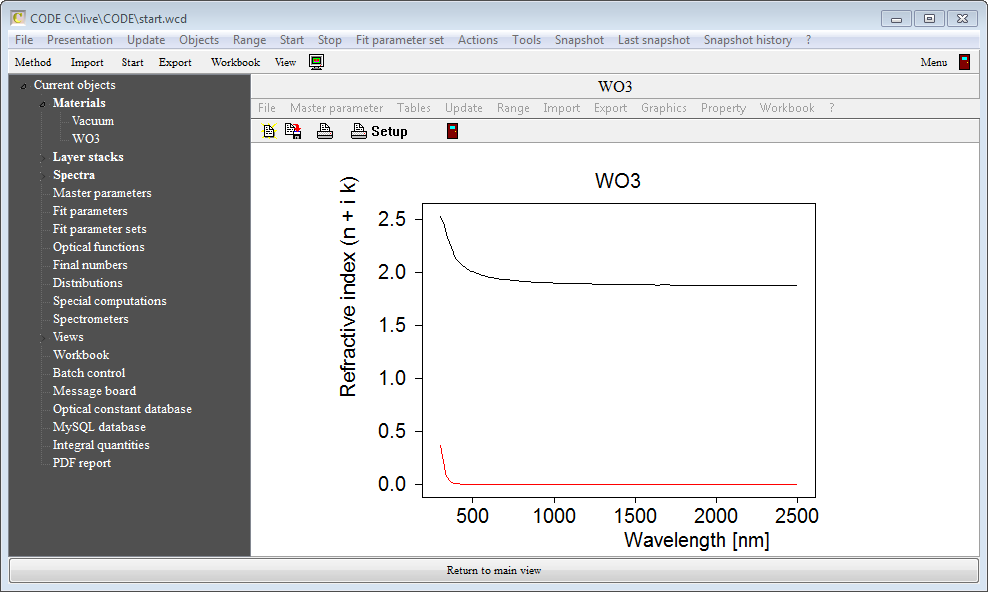
Repeat the steps described above for the k values which are collected in a similar object.Once you have done that the final object is this:
Now try if the object really interpolates values. Use the command 'Master parameter / set value' and type in the number 40. Then press Update. The new data should look like this:
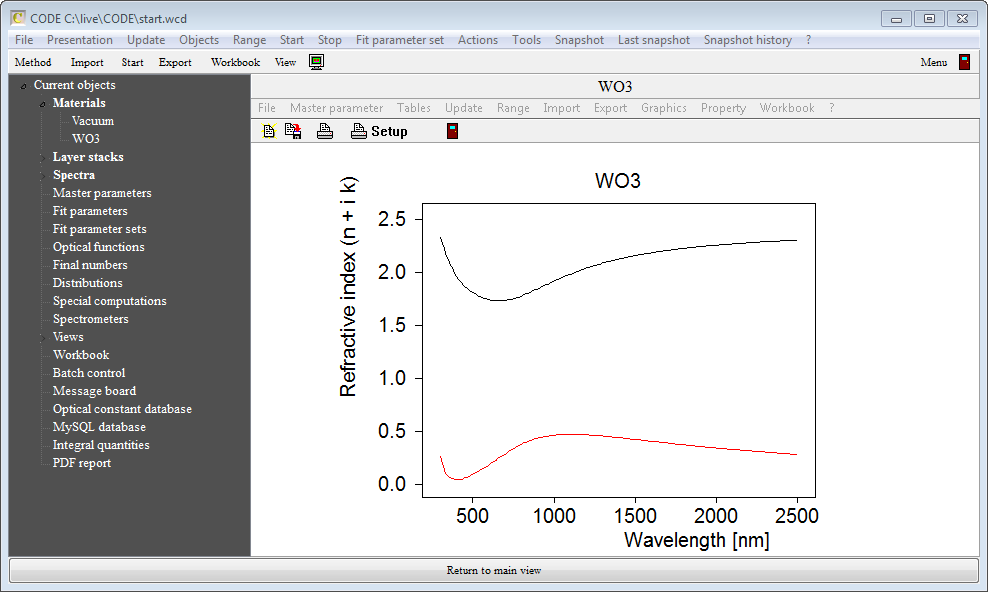
We can now use this material object to deliver n and k values for the charge range 0 ... 68.
Importing data from workbook table
If you have a data table in Excel format already the import is much faster (because you did the tedious work before). Open the workbook and select the top left corner of the data block you want to import:
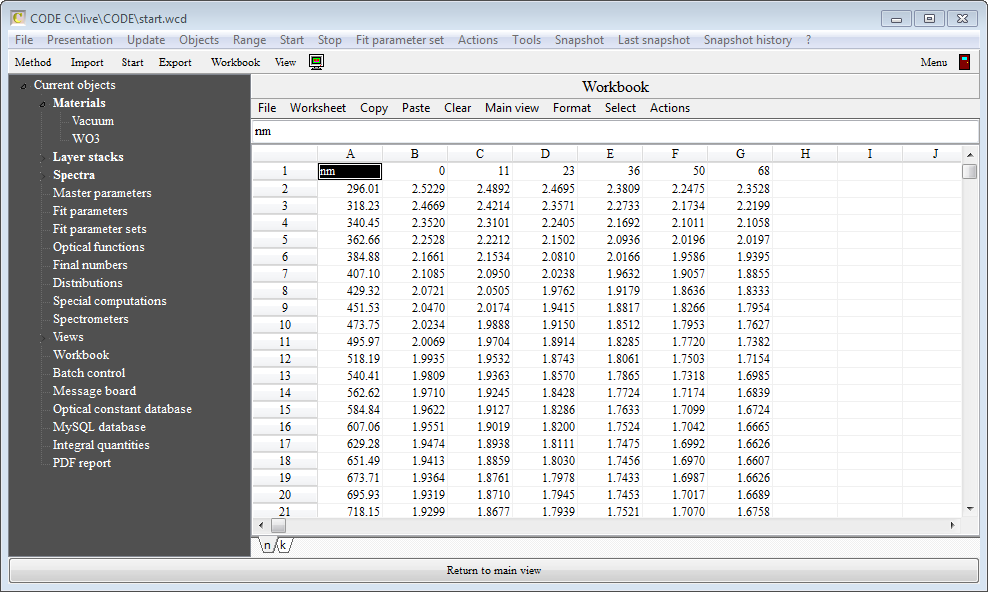
As described above, open the subwindow that will collect the n values:
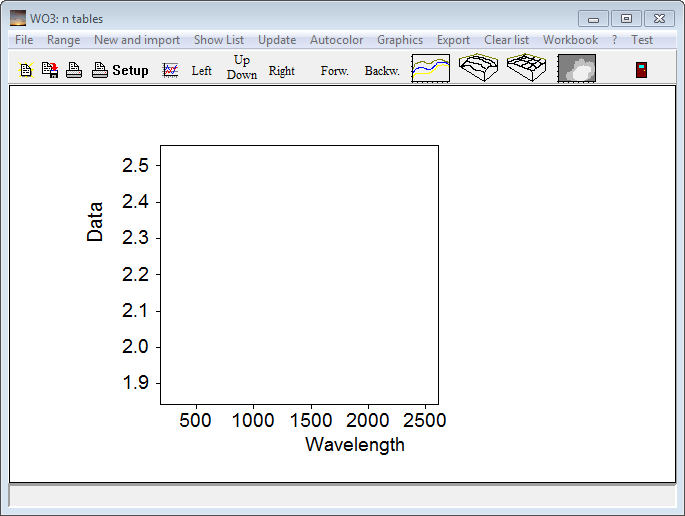
Execute the command 'Workbook / Import _ p1 p2 ... x y1 y2 ... downwards' and press 'a' for automatic scaling:
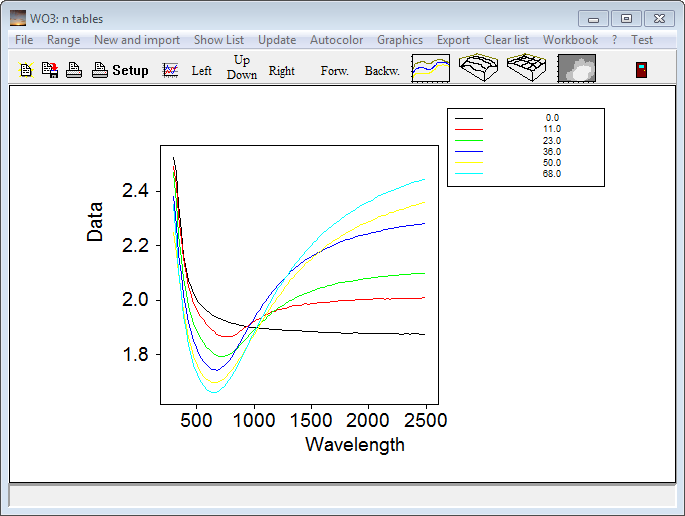
Very important: Click on 'Range' and set 'nm' as spectral unit in the following dialog:
Then click on 'Show list' which opens the list of spectra. In this list, click on 'Set all spectral units' and choose 'nm'. This action sets 'nm' as spectral unit for all spectra (see last column):
You can now close all subwindows and import the k data in the same way.