Objects of this type compute the average absorption and scattering characteristics of collections of spheres. The main window is this:
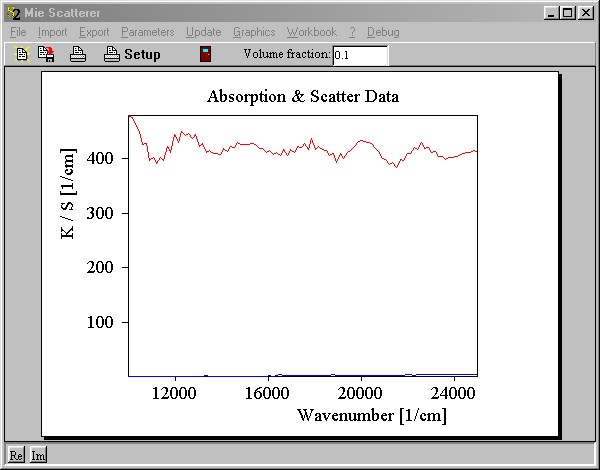
Like with general scatterers you can import rt-files and set the volume fraction of the scattering particles. In addition, you can compute your own absorption and scattering data using an external Mie program (the quite old-fashioned DOS program RTMIE, delivered with SPRAY) which will do the computational work.
In a subwindow of Mie scatterer objects which you open by the Parameter command you can set the required parameters for the Mie computation:
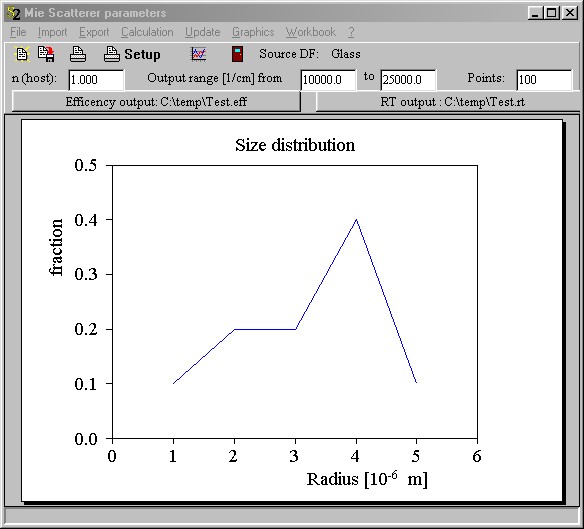
You have to specify the following items:
•The optical constants of the sphere material: Open the list of dielectric functions and drag an entry to the text field right to the label 'Source DF:'. Make sure that the name of the right dielectric function is displayed (in the example above: Glass).
•The refractive index of the host material surrounding the spheres: Enter the value of the refractive index in the field next to the label 'n(host)'. The refractive index must be constant and real. If you use the generated scattering data later on in a SPRAY simulation you must use the same surrounding refractive index as used here in the Mie computation.
•The wavenumber range for the output data: For historical reasons the spectral unit to be used in Mie computations must be wavenumbers. You have to specify the minimum and maximum value and the number of data points.
•The files for the computed efficiency data (see below) and the RT output data (that are later used in SPRAY).
•The radius distribution of the spheres: The Mie computations are performed for a distribution of sphere sizes which is displayed in the graph of the window. The radius distribution shown above has the following meaning: If you take a collection of 1000 spheres you will find 100 particles with radius 1 micron, 200 with radii 2 and 3 microns, 400 with radius 4 microns and 100 with radius 5 microns. You can use the Import command to import the radius distribution from a file. Alternatively you can import a distribution from the workbook using the Workbook commands. Note that the sphere radius has be entered in 'm'.
In order to perform Mie computations with the RTMIE program the program file rtmie.exe must be present in the directory c:/mie. This is an old FORTRAN program running in a DOS box. It cannot handle long filenames and filenames or directory names with blanks correctly. Hence you should be careful with the choice of filenames in your Mie work.
Activation of the Calculation command starts the following actions:
•SPRAY will create files that contain the dielectric function and the radius distribution of the spheres.
•The filenames and the other parameters are written to a small textfile called rtmie.ctl which is stored in the fixed directory c:/mie.
•RTMIE is started. It will run in a DOS box, load the input data, show the progress of the work and finally create the required output data.
When the RTMIE program quits you can start to use the computed RT data for your SPRAY computations.